Introduction to the Brain’s Role in the BodyThe brain stands as the cornerstone of our body’s intricate control system. This paramount organ, composed of approximately 86 billion neurons, serves as the command center orchestrating a myriad of physiological and psychological processes essential for our survival and well-being. It is responsible for the regulation and integration of numerous bodily functions, ranging from muscle control and coordination to the processing of sensory information, ultimately influencing our actions and behaviors.
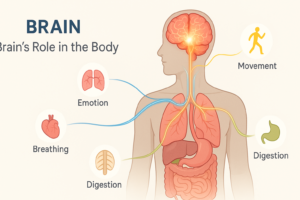
One of the primary roles of the brain is muscle control. Through a complex network of neural pathways, the brain sends signals that coordinate voluntary and involuntary muscle movements. This enables us to perform everyday activities, from walking and eating to more sophisticated tasks such as playing a musical instrument or participating in athletic endeavors. The motor cortex, a region of the brain, plays a pivotal role in planning, initiating, and executing these movements.
In addition to muscle control, the brain is pivotal in sensory integration. It receives and processes information from our sensory organs – eyes, ears, skin, taste buds, and olfactory receptors. This sensory data is then interpreted by various brain regions, allowing us to perceive, interpret, and respond to our environment. The thalamus acts as a relay station for this sensory information, while the occipital, temporal, and parietal lobes specialize in processing visual, auditory, and tactile inputs respectively.
Beyond these fundamental functions, the brain is integral in decision-making and emotional regulation. The prefrontal cortex is involved in complex cognitive processes such as reasoning, problem-solving, and decision-making. Meanwhile, the limbic system, encompassing structures like the amygdala and hippocampus, governs our emotional responses and memory formation. These combined functions underline the importance of brain health in ensuring our overall well-being.
Understanding the brain’s multifaceted roles emphasizes why maintaining its health is crucial. The subsequent sections will delve into how nutrition and other factors can help sustain and enhance brain function, safeguarding our body’s control center and promoting a higher quality of life.
The Importance of Brain Health

Brain health is essential for overall well-being, directly influencing cognitive performance, emotional balance, and mental clarity. The brain acts as the control center of the body, orchestrating functions that range from daily activities to complex decision-making processes. A healthy brain ensures that one’s cognitive abilities remain sharp, facilitating the processing of information, learning, and memory retention. These aspects are vital not only for professional and academic success but also for personal growth and quality of life.
Emotional balance is another critical component of brain health. The brain regulates emotional responses and maintains mental harmony, which is crucial for managing stress, anxiety, and depression. By ensuring the brain’s optimal functioning, individuals can better navigate emotional challenges and sustain positive mental health. Furthermore, mental clarity, the ability to think clearly and make well-informed decisions, is heavily dependent on the brain’s health. This clarity affects daily routines and long-term planning, impacting personal and professional lives.
The long-term benefits of maintaining brain health are vast. A well-functioning brain helps delay or prevent cognitive decline, enhancing one’s cognitive reserve and reducing the risk of memory loss and dementia. Additionally, good brain health is linked to a lower incidence of neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. These conditions, often associated with aging, can significantly diminish an individual’s quality of life, underscoring the importance of proactive brain care.
Neglecting brain health can lead to severe consequences. Cognitive decline, characterized by gradual memory loss and difficulty in thinking, can impede daily functioning and reduce independence. The risk of developing neurological disorders increases, leading to challenges that can strain families and healthcare systems. Therefore, prioritizing brain health is crucial for maintaining cognitive performance, emotional stability, and overall life satisfaction, making it a key component of holistic health.
Aging and the Brain: Challenges and Changes
As we age, our brain undergoes several alterations that can significantly impact cognitive function. One of the key changes observed in the aging brain is a general slowing down of cognitive processes. This includes tasks such as problem-solving, decision-making, and processing speed. These age-associated changes are not uniform and can vary widely among individuals, influenced by genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors.
Another critical aspect of brain aging is decreased neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to form and reorganize synaptic connections. Neuroplasticity is fundamental for learning and memory, and its decline can lead to difficulties in acquiring new skills or information. This reduction in plasticity can be associated with a decrease in certain neurotransmitters and loss of synaptic connections, which are more pronounced in aged brains.
Moreover, the aging brain is more susceptible to neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. These conditions are characterized by the progressive loss of specific neurons and the accumulation of abnormal protein aggregates, such as amyloid plaques and tau tangles in Alzheimer’s disease. The exact causes of these diseases are complex and multifactorial, involving genetic predispositions and environmental exposures. However, the prevalence of these conditions increases significantly with age, posing a major challenge to the aging population.
Proactive measures can help mitigate age-related impacts on brain function. Engaging in regular physical activity has been shown to promote brain health by enhancing blood flow, reducing inflammation, and supporting the growth of new neurons. Cognitive exercises, including puzzles, reading, and lifelong learning, can help maintain and even enhance cognitive function. Furthermore, a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, healthy fats, and essential vitamins plays a crucial role in supporting brain health and mitigating oxidative stress, which is partly responsible for aging.
By understanding the challenges posed by aging on the brain and taking proactive steps, individuals can better maintain their cognitive function and quality of life. Simple yet consistent practices can indeed make a substantial difference in promoting brain health well into old age.
The Role of a Nutritious Diet in Brain Health
A balanced and nutritious diet plays a pivotal role in maintaining brain health and optimizing cognitive function. Among the essential nutrients, omega-3 fatty acids are particularly significant. Predominantly found in fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, these polyunsaturated fatty acids are known for their critical role in the development and functioning of the brain. Omega-3s support the structural integrity of brain cells and modulate synaptic plasticity, thereby enhancing learning capabilities and memory.
Antioxidants are another essential component of a brain-healthy diet. Found in a variety of fruits, vegetables, and nuts, antioxidants like vitamin C, vitamin E, and flavonoids help mitigate oxidative stress. Oxidative stress is an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in the body, which can lead to cellular damage in the brain. By neutralizing free radicals, antioxidants protect neurons from damage and can potentially lower the risk of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s
Vitamins and minerals are also indispensable for brain health. For example, B vitamins, including B6, B12, and folic acid, play key roles in the synthesis of neurotransmitters, which are chemicals that transmit signals in the brain. These vitamins help in the production of serotonin, dopamine, and other neurotransmitters that regulate mood, sleep, and cognitive functions. Iron and zinc are minerals that facilitate oxygen transport and enzyme function, respectively, further supporting overall brain activity.
The mechanisms behind how these nutrients enhance cognitive function are multifaceted. Omega-3 fatty acids aid in reducing inflammation and fostering communication between brain cells. Antioxidants safeguard against cellular stress and neuronal damage. Vitamins and minerals aid in the production and function of neurotransmitters, keeping the brain’s communication system efficient. By understanding and integrating these nutrients into our diets, we can actively contribute to long-term brain health and cognitive performance.
 Key Foods for Brain Health
Key Foods for Brain Health
Maintaining optimal brain health requires careful attention to one’s diet. Specific foods have been identified for their brain-boosting properties, contributing to cognitive function, memory retention, and overall mental well-being. An essential category are fatty fishes, such as salmon, trout, and sardines, rich in omega-3 fatty acids. These essential fats fortify brain cell membranes and support neuron function, fostering better communication between brain cells.
Berries, especially blueberries, are another powerhouse for the brain. Packed with antioxidants, they protect the brain from oxidative stress and reduce inflammation, which is beneficial for maintaining cognitive functions. Regular consumption of berries has been linked to slowed brain aging and improved memory.
Nuts and seeds are indispensable, particularly walnuts and flaxseeds, which are laden with antioxidants, healthy fats, and vitamin E. These elements play a pivotal role in protecting the brain from oxidative damage and enhancing cognitive performance. Additionally, regular intake of nuts and seeds supports overall mental sharpness and assists in the reduction of age-related cognitive decline.
Leafy greens, including spinach, kale, and broccoli, are rich in brain-healthy nutrients like vitamin K, lutein, folate, and beta carotene. These vital components are associated with slower cognitive deterioration and are believed to help in protecting the brain from damage.
Whole grains such as oats, barley, and brown rice contribute significantly to brain health by providing a steady supply of glucose, the brain’s main energy source. These grains also contain fiber and essential vitamins, which support good circulation and ensure an adequate supply of nutrients to the brain.
Incorporating these foods into a balanced diet doesn’t have to be challenging. Simple adjustments, such as adding a handful of berries to breakfast cereal, including a portion of leafy greens in your lunch, snacking on nuts, or choosing fatty fish for dinner, can make a substantial impact. By prioritizing these brain-supportive foods, individuals can enhance their cognitive health and protect their brains against age-related decline.
Lifestyle Tips for Enhancing Brain Function
While a nutritious diet is essential, various lifestyle factors also significantly impact brain health and functionality. Integrating these elements into your daily routine can help optimize cognitive performance and maintain mental well-being.
First and foremost, regular physical exercise is a cornerstone for enhancing brain function. Engaging in activities like walking, swimming, or yoga can boost cardiovascular health, which in turn ensures a consistent supply of oxygen and nutrients to the brain. Aerobic exercises, in particular, are linked to increased hippocampal volume, a critical brain region associated with memory and learning.
Mental stimulation also plays a crucial role. Activities such as reading, solving puzzles, or learning a new skill can foster neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to form new neural connections. These mentally engaging exercises keep the brain agile and may delay the onset of cognitive decline.
Adequate sleep is another pivotal factor. During sleep, the brain undergoes vital processes of repair and memory consolidation. Chronic sleep deprivation can impair cognitive function, decision-making, and emotional regulation. Ensuring 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night is crucial for maintaining mental acuity.
Effective stress management is equally important. Prolonged stress can trigger the release of cortisol, which, in excess, may adversely affect brain cells and shrink the prefrontal cortex, the area of the brain responsible for executive functions. Meditation, deep-breathing exercises, and mindfulness practices can mitigate stress and promote a healthier neural environment.
Lastly, social engagement should not be overlooked. Interacting with others, participating in social activities, and maintaining strong relationships create emotional support systems that are beneficial for mental health. Socially active individuals often display greater psychological resilience and cognitive sharpness.
Incorporating these lifestyle tips can substantially enhance brain function, contributing to greater cognitive longevity and overall mental wellness.
`


